Your company can lose important data in a crisis, and operations might end abruptly. Nevertheless, chaos doesn’t have to control your company. A well-crafted Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) within the framework of ISO 27001 compliance acts as a lifeline for organizations to recover quickly and effectively from disasters, minimizing downtime and protecting sensitive information.
To be more precise, this guide elaborates on what an ISO 27001 Disaster Recovery Plan entails, why it is essential for compliance, and how organizations can implement it effectively.
What Is ISO 27001 Disaster Plan?
An ISO 27001 disaster recovery plan outlines what you should do in the event of an information security incident. An effective ISO disaster recovery strategy is customized to meet the needs of the firm.
A disaster recovery plan puts in place a few safeguards to guarantee that all data is routinely and safely backed up. It ensures that the organization is prepared to handle disruptions without compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of its information assets. This not only protects the organization from potential legal and financial repercussions but also strengthens customer trust and confidence in the company’s ability to safeguard its data.
One of the major methods of the Disaster plan is the swift restoration method. Putting this in place and using cloud computing, rapid data recovery, and encryption, may lessen the effects of an information security event.
Although a disaster plan is effective, it is important to confirm that the plan works as effectively as possible to restore IT services within the agreed-upon timeframe; it functions similarly to business continuity insurance.
Overview Of ISO 27001 Disaster Recovery Plan-
Considering the necessity, the ISO 27001 standard helps in the development of a structured and precise recovery strategy. Among the many factors that comprise an all-encompassing strategy are defining roles and duties for every phase of the procedure, pre-documenting vital assets, and regularly testing your recovery plans. Organizations that consider all of the above factors are better equipped to bounce back swiftly from unforeseen disruptions or natural disasters.
Let’s back up-
- Establish A Business Continuity Management
One of the most important initial steps in creating an ISO 27001 disaster recovery strategy is setting up a business continuity management system (BCMS). Businesses are provided with the rules, methods, and processes necessary to effectively recover from disruptions by a BCMS. This extensive system is adaptable to the unique requirements and goals of the business.
For instance, some businesses could acquire secondary locations that can serve as backup facilities or provide fail-safe data backups. Regardless of the type of event—natural or not—having a BCMS in place guarantees that the company has all the tools and data needed to react appropriately.
- Identifying Risk Sources
Finding risk sources may be difficult since there are so many factors to consider! Nonetheless, taking aggressive action is an essential first step. Consider the risks such as floods that can cause havoc in your everyday life; similarly, cyberattacks might target your company’s computer networks.
Both man-made and natural disasters can do just as much harm in different ways. Having an understanding of the typical sources of hazards gives you a head start when creating plans to manage them. After determining the main sources of risk, you may proceed to create plans to mitigate the effects of the risks and prevent their outcomes.
A few calamities may be:
- Flames
- Cyberattacks
- Information disclosure
- Trend shift Power outages
- Plan failure
- Develop Mitigation Strategies
Creating mitigation plans is crucial to minimizing the harm caused by unforeseen interruptions. For instance, it might be quite helpful to have a backup generator in case of a power loss so that computers and communications networks remain operational.
Important data won’t be lost when an office closes or is destroyed thanks to offsite data storage. In times of disaster, having backup communication channels in place ensures continuity.
- Build Response And Recovery Plans
Following the creation of mitigation strategies, reaction and recovery plans must be created. The actions that need to be done right away following a disruption are described in the reaction plan.
- Getting a Backup Of Your Important Data
What would happen if a disk failure or other technical issue caused you to lose your clients’ data? It might be disastrous and cause your company to fail. To make sure that this doesn’t happen and that recovery is feasible after any disaster, a secondary IT infrastructure needs to be employed to establish a backup of critical data.
This additional security for the data of your business keeps you prepared in case of disaster.
- Understanding Critical Functions
Any company must determine which elements are essential to its survival. Businesses may determine the essential tasks of their personnel, machinery, websites, cash registers, and customer data, and make plans for unforeseen circumstances by looking at these components.
What Is Included In The ISO 27001 Disaster Plan?
- Recovery Flowchart
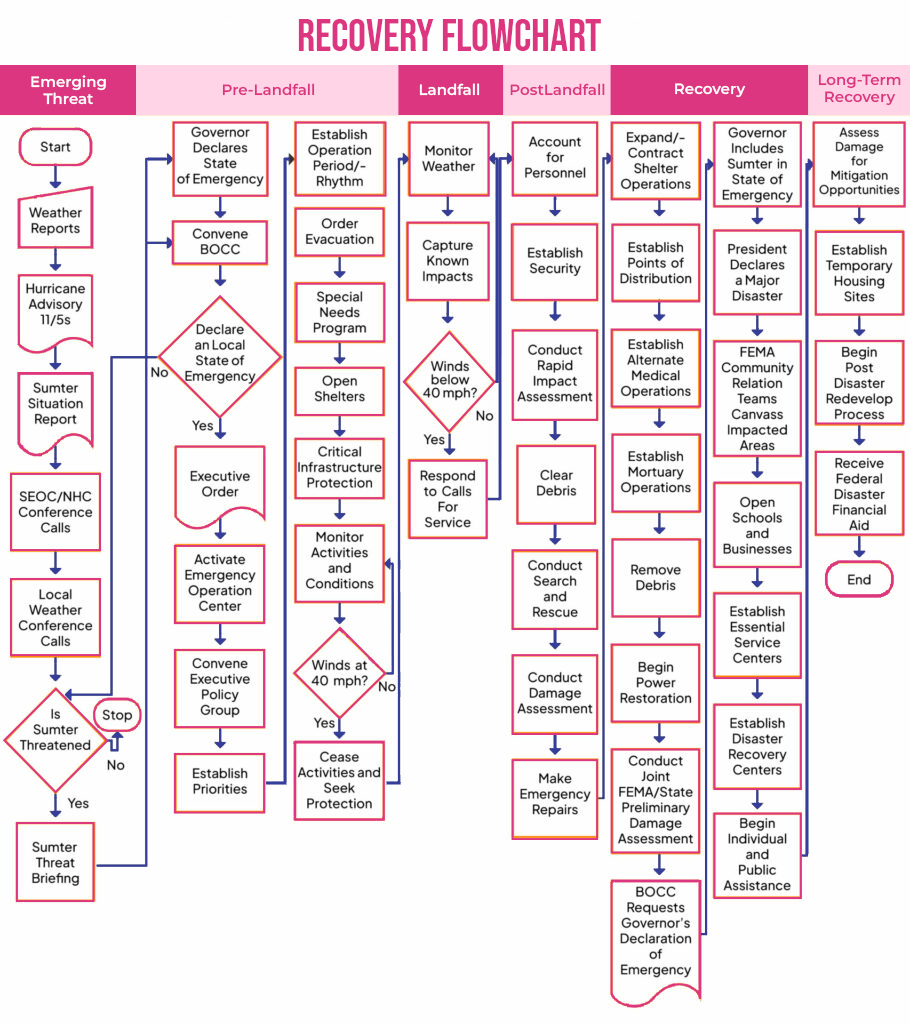
A flowchart that illustrates your company’s disaster recovery plan explains what procedures it will take to resume operations in the case of a significant system failure. This diagram lists the precise activities that must be accomplished, along with who will be in charge of each activity and what resources—such as personnel, tools, and software—will be needed to do them.
Creating an effective recovery plan can be challenging, but making use of a flowchart will guarantee that all required actions are carried out efficiently and in the right order.
For instance, an IT team may find it difficult to manage the first few steps after a disaster, such as a system inventory and data backup, but a well-made flowchart will specify exactly which activities must be finished for the overall recovery plan to be implemented without a hitch.
In the case of a tragedy, going through each step on the chart one by one should give you peace of mind that everything has been taken care of.
- Recovery Team
A disaster recovery team can reduce the likelihood of catastrophic losses while making all the difference. Consider Hurricane Katrina as an example. Companies that had prepared ahead of time and responded promptly to the storm were able to assist their staff and resume operations far more swiftly than those that did not.
The people on a disaster recovery team are in charge of resuming operations in the case of a significant system breakdown. In the case of a significant system failure, it describes the actions that must be performed to restart company operations. The plan’s implementation and operations restoration fall within the purview of the disaster recovery team.
This specialized team is crucial for spotting possible dangers, evaluating current weaknesses, and developing strategies to assist in guaranteeing everyone’s safety during emergencies.
- Incident Management Process
An organization’s guidelines for handling occurrences are called incident management procedures. This covers equipment malfunctions, power outages, and fires and floods. Reducing the impact of an event on the company is the aim of an incident management procedure.
Assessing and establishing the incident’s severity level is the first stage in incident management. This will enable you to prepare your response. Typical answers include the following:
- Notifying the emergency services
- resuming activities as quickly as feasible
- Examining the safety protocols
- Speaking with staff members
- Assessment Form
One instrument that may be used to record the damages done to a property is a damage assessment form. Property owners, insurance companies, and anybody else who needs a record of the injuries might utilize this form. The data obtained on the form is utilized to estimate the cost of repairs and the resources that will be required.
The following items need to be listed on a damage assessment form:
- Date and Property Location
- Name of the Insurer; Damages Photographs
- Description of Damage and Approximate Replacement or Repair Cost
- Datacenter Resilience
When developing a robust data center, there are several factors to take into account. The physical infrastructure, which includes network connectivity, backup cooling, and electricity, is crucial. Strong disaster recovery and backup procedures are also required, including offsite data storage and backups to enable speedy restoration in the case of an outage.
For instance, in the event of a power outage or other emergency, the facility’s electric system—which is powered by a high-voltage UPS system and backup generator—must continue to function properly.
Many businesses incorporate dependable cloud-based storage solutions into their data-resilience strategies in addition to this physical layer of security. This facilitates fast recovery when necessary and serves as protection against hardware failure.
Having a well-thought-out plan in place for handling interruptions is also crucial. The disaster recovery and backup plans should be known to the staff, and routine testing should be done to make sure everything is functioning as it should.
- Risk Assessment
Assisting communities and companies in lowering their chance of encountering a disaster is one of the primary goals of disaster risk assessment. Mitigation measures can be put in place to assist lessen the possibility or effect of a disaster by identifying the regions most at risk.
The types of losses that could be anticipated during a disaster might also be determined via disaster risk assessments. Decision-makers can more efficiently allocate resources for readiness and reaction with the use of this information.
- Emergency Alert And Escalation
There is little time to respond appropriately once a major calamity occurs. An emergency warning and escalation strategy might be useful in these situations. This policy should include how staff members react to danger and how to swiftly evacuate them before things become worse.
- Backup Storage & Security
One size does not fit all when it comes to backup storage and security. To reduce vulnerability, you should use encrypted, remote backups to restrict exposure, cloud-based backups with robust encryption methods, and physical backups kept away.
You should also think about the safety precautions you have in place for both traveling and resting. Strong Network Intrusion Detection systems can identify threats against your data more rapidly, and multi-factor authentication procedures can assist prevent unwanted access. To defend against malicious attacks and natural calamities, you need an efficient backup storage and security plan.
Why Is ISO 27001 Disaster Plan Important In Compliance?
- Maintaining ISO 27001 Business Continuity
A disaster recovery plan ensures that essential business functions can continue during and after a crisis, such as a cyberattack, natural disaster, or system failure. According to a study by the Business Continuity Institute (BCI), 73% of organizations have experienced at least one disruption in the last 12 months, with the average downtime costing $300,000 per hour. By having a robust disaster recovery plan, businesses can minimize downtime and keep operations running smoothly, aligning with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Ensuring Data Security
The 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM revealed that the average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million globally. Implementing a disaster recovery plan as part of ISO 27001 compliance helps safeguard sensitive data and reduces the risk of costly breaches.
- Complying With Regulations
Failure to recover quickly from disruptions can lead to non-compliance, resulting in fines and legal penalties. A report by Deloitte indicates that non-compliance costs organizations 2.71 times more than the cost of maintaining compliance. By having an ISO 27001-compliant disaster recovery plan, businesses can avoid these penalties and ensure they meet all regulatory requirements.
- Safeguarding From Financial Losses
An ISO 27001 disaster recovery plan helps mitigate financial losses by minimizing downtime and enabling quick resumption of operations. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) reports that 40% of small businesses do not reopen after a disaster, and 90% fail within two years if they cannot recover quickly.
- Protecting Company’s Reputation
Customers expect reliability, and any prolonged downtime or data breach can lead to a loss of trust. The Edelman Trust Barometer found that 81% of consumers need to trust a brand to buy from them. An ISO 27001 disaster recovery plan demonstrates a company’s commitment to security and reliability, helping to maintain customer trust and protect the company’s reputation during challenging times.
- Increased Productivity
A disaster recovery plan not only helps in managing crises but also contributes to overall productivity. By ensuring that employees can continue their work even during a disaster, the plan reduces disruptions and maintains operational efficiency. According to a study by IDC, the average annual cost of unplanned application downtime is $1.25 billion to $2.5 billion for Fortune 1000 companies.
Who Creates The Disaster Recovery Guidelines For Compliance?
Businesses must adhere to the rules and regulations established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to adequately plan for disruptions. Through collaboration with agencies such as OSHA, WHO, and ILO, the ISO guarantees that firms comply with its standards and helps avert disasters from starting or worsening. This is intended to provide you with the assurance you require to customize a disaster recovery strategy for your company.
How To Implement The ISO 27001 Disaster Plan?
Developing the Plan: Create detailed documentation that includes all necessary procedures, responsibilities, and resources.
Training Staff: Ensure that all relevant employees are trained on their roles within the plan.
Testing the Plan: Conduct regular drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of the plan.
Review and Update: Continuously review and update the plan to reflect changes in the business environment or IT infrastructure.
Get ISO 27001 Automated With Socurely
Socurely has you covered if the intricacies and technical terms of compliance are overwhelming you! We relieve you of the stress of human work by providing an automated solution for your ISO 27001 certification, which includes everything from creating policies to monitoring security measures.
Not only that, but our in-app staff security training function also helps your personnel gather defenses against data breaches by keeping them up to date on the newest cybersecurity protocols. Allow us to facilitate this experience for you! Schedule a demo with Socurely right now to see its true enabling potential in action, and feel free to ask any questions you may have.
Conclusion
A well-implemented ISO 27001 Disaster Recovery Plan is not just a compliance requirement; it’s a critical component of your organization’s resilience strategy. By understanding the plan’s elements and how to implement it effectively, you can safeguard your business from potential disasters and ensure continuity in the face of unexpected disruptions.
FAQ
What is the ISO standard for disaster recovery?
The ISO standard for disaster recovery is part of ISO 27001, which addresses the requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Who Needs The ISO 27001 Disaster Plan?
Any organization that seeks ISO 27001 certification or aims to protect its information assets against disasters needs an ISO 27001 Disaster Recovery Plan.
How Compliance Is Benefited With ISO 27001 Disaster Plan?
Compliance with ISO 27001 is enhanced by a disaster recovery plan as it ensures that the organization can maintain information security even during and after a disaster.







